What Is a Newborn Baby's Heart Valves Upside Down Called
Aortic stenosis is a term used to describe congenital heart defects that obstruct blood flow from the heart to the body. Significant aortic stenosis is relatively uncommon, affecting near 6 of every grand babies built-in, occurring more ofttimes in boys. It can occur alone, that is, without other center problems, or in clan with bicuspid aortic valve, coarctation of the aorta, ventricular septal defect, mitral valve aberration, and less commonly with atrial septal defect or complete atrioventricular septal defect. University of Michigan C.Southward. Mott Children'south Hospital is an international referral center for children with complex congenital heart disease. Our expertise in diagnosing and treating aortic stenosis includes specialization in fetal diagnosis and intervention likewise equally treatment and long term care for children diagnosed as infants.
What is aortic stenosis?
In the normal eye, scarlet claret returning from the lungs flows from the centre's left upper sleeping room called the left atrium (1) through the mitral valve to the left ventricle (two) where information technology is pumped through the aortic valve and out to the trunk. When a child has aortic stenosis, the surface area where claret exits the heart'south lower left chamber is as well narrow. Usually, the aortic valve itself is affected and this is chosen valvar aortic stenosis. Come across (3) in the figure beneath. This problem tin can be caused past fusion of the valve leaflets, a condition called bicuspid aortic valve. 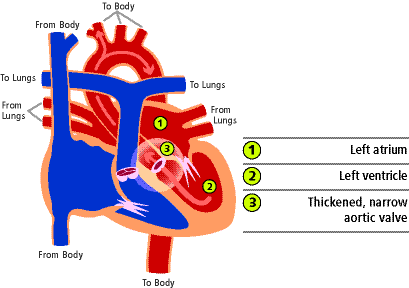 In more than severe forms of valvar stenosis, the fibrous ring of tissue that supports the valve is also small and underdeveloped. Subvalvar aortic stenosis is the term used when the narrowed area is below the valve (one) in the effigy beneath.
In more than severe forms of valvar stenosis, the fibrous ring of tissue that supports the valve is also small and underdeveloped. Subvalvar aortic stenosis is the term used when the narrowed area is below the valve (one) in the effigy beneath.  Supravalvar aortic stenosis is the term used when the narrowed area is above the valve (1) as shown in the effigy below.
Supravalvar aortic stenosis is the term used when the narrowed area is above the valve (1) as shown in the effigy below. 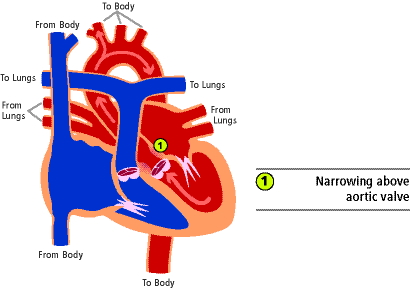
How will this problem touch my kid's health?
Like nearly middle defects, aortic stenosis does not have an adverse effect until after a baby is born. The wellness furnishings of aortic stenosis are related to the degree of the narrowing, valve leaks, and if at that place are other centre defects. The degree of narrowing is measured as the pressure difference across the aortic valve, which is referred to as the gradient. The higher the slope, the greater the trouble, since the left centre has to work much harder to pump blood to the body. Based on the gradient, aortic stenosis is diagnosed as either lilliputian, mild, moderate or astringent. Critical aortic stenosis is a term used in newborns with very severe narrowing , requiring handling before long after nativity. Over time, if the trouble is not treated, this overwork causes a thickening of the center muscle chosen ventricular hypertrophy. Eventually, the musculus becomes damaged resulting in left-sided middle failure and abnormal centre rhythms. When the aortic valve is affected, there may exist leaking of the valve in addition to the narrowing. Terms used to describe the severity of valve leakage include trivial, balmy, moderate, and severe. The more the valve leaks, the harder the heart and the left ventricle have to work to pump blood out to the trunk. The combination of pregnant leakage and narrowing can crusade a nifty deal of stress on the heart. The natural history of aortic stenosis is that it tends to become more severe over fourth dimension. For this reason, periodic visits to a pediatric cardiologist are of import. If the narrowing is piffling and caused by a bicuspid aortic valve it may not progress. In a baby born with critical aortic stenosis, the opening is then small that the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the baby'southward needs. Unless the problem is treated early, the baby volition develop problems with shock and congestive heart failure. A medication called prostaglandin may exist used to keep the ductus arteriosus patent or open. The ductus arteriosus is a small-scale blood vessel that connects the pulmonary artery with the aorta and provides a way for blood to become out to the body. The blood that exits the center by the ductus arteriosus bypasses the lungs so the babe may look a little blue. Children with aortic stenosis are at increased adventure for subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE). This is an infection of the heart caused by bacteria in the blood stream. It tin occur after a dental or other medical procedure and tin largely be prevented by a dose of antibiotic prior to the procedure. Exercise recommendations are best made by a patient'due south doctor then that all factors can be included in the decision. Children with aortic stenosis can participate in recreational physical activities only are usually restricted from competitive and vigorous able-bodied activities. If the aortic stenosis is footling, they may be permitted to participate in competitive athletics but volition need to run across their cardiologist regularly to make certain that the narrowing has not progressed.
Diagnosis of aortic stenosis
Prenatal diagnosis: Fetal diagnosis of aortic stenosis is made by an echocardiogram of the babe's centre and can be made as early every bit 16 weeks into the pregnancy. An echocardiogram of the center is done when a possible problem is identified during a routine prenatal ultrasound or because of a family history of built heart disease. The University of Michigan Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment Eye offers comprehensive fetal diagnosis and handling alternatives for unborn babies with aortic stenosis. Symptoms: Symptoms of aortic stenosis are related to the caste of narrowing, leakage, and the presence of other heart bug. Mild aortic stenosis usually does not cause eye-related symptoms. More severe aortic stenosis may cause chest pain that is related to exercise, decreased stamina, palpitations or "skipping beats", and/or fainting. Undetected aortic stenosis can cause sudden death during vigorous physical exertion. Critical aortic stenosis in an baby tin can cause congestive center failure with symptoms of poor feeding, rapid animate, clammy sweating, lethargy, and/or irritability. Physical findings: Aortic stenosis is often diagnosed due to the presence of a heart murmur. Infants may have symptoms of congestive heart failure as described above equally well as weak pulses. Medical tests: The gold standard for diagnosis is an echocardiogram. Cardiac catheterization is done if there are whatever questions not clearly answered by the echocardiogram and may besides exist done for therapeutic purposes, that is, to perform a airship dilatation or angioplasty.
Handling for aortic stenosis
For select patients diagnosed with aortic stenosis prenatally, fetal intervention can exist an option. For children diagnosed afterwards birth, or for babies for whom fetal intervention was not an option, treatment is adamant past many factors including the location of the narrowing, severity of narrowing, associated cardiac issues, symptoms, age, and size. Valvar aortic stenosis can exist treated surgically or by airship dilation, a procedure done in the cardiac catheterization lab. For the almost part, other types of aortic stenosis are treated surgically. These procedures are done to open up the area of obstacle to decrease the amount of work the left ventricle has to do to go blood out to the body. This helps to protect the heart muscle from overwork and evolution of heart failure and/or abnormal heart rhythms. Balloon angioplasty for valvar aortic stenosis: Aortic stenosis often progresses over fourth dimension. Balloon angioplasty may exist the only intervention required but is often used as a temporary means to delay open up-middle surgery. This procedure is done in the heart catheterization laboratory. During the procedure, catheters (thin plastic tubes) are placed into the big claret vessels in the legs and gently guided to the heart. The catheter tip is placed across the aortic valve and the balloon tip is inflated. The balloon gently dilates the narrowed surface area. The incidence of complications is low and includes damage to the femoral artery, haemorrhage, perforation, and aortic valve leakage. Surgery for valvar aortic stenosis At that place are a number of surgical options that may exist utilized: Surgical valvotomy: This procedure is a type of repair to the aortic valve in which the valve itself is stretched to allow amend blood flow. During surgical valvotomy, an incision is made downwards the center of the breastbone. The heart is stopped for a cursory period of time while the torso is supported with a heart lung bypass machine (ECMO). The defect is then fixed by making an incision into the ascending aorta where it exits the left ventricle. An instrument called a dilator is then placed through the aorta and through the opening of the aortic valve stretching it. Progressively larger dilators are used until the valve is opened every bit much every bit possible without overstretching the valve which would let it to leak blood backwards into the ventricle. Valve replacement surgery: Sometimes the aortic valve is too narrow or too leaky to repair. When this happens the aortic valve will eventually demand to be replaced. The goal is to place when the valve role is poor enough to cause overwork for the eye, but earlier in that location is permanent damage. This is washed through the history and concrete examination as well as heart tests done during routine clinic visits. There are several types of valve replacement procedures and the choice of which performance is best for a child is decided through discussions with the parents, the pediatric cardiologist, and the pediatric cardiac surgeon. Valve replacements lone are non always enough to relieve the narrowing out the ventricle. Sometimes the whole area leading out of the ventricle to the aorta is too small. The supporting structure of the valve, called the valve annulus, may be besides narrow even if the leaflets are opened upwards as far as possible. In these cases the valve replacement is performed with a procedure chosen a Konno procedure. This involves enlarging the left ventricular outflow tract and the valve ring. It is done through an incision into the outflow tract of the right ventricle and the septum or wall between the right and left ventricles. A patch is placed in this area that enlarges it. The Konno procedure tin can be done with any blazon of aortic valve replacement. Surgery for subvalvar aortic stenosis: Subvalvar stenosis can be caused past a discrete membrane or by thickened muscle. Repair for discrete membranous stenosis is done to prevent damage to the aortic valve and to preserve left ventricular function. An incision is made down the center of the breastbone and the heart is stopped for a brief period of time while a heart-lung bypass car supports the body. An incision is made in the aorta and the surgeon looks through the valve to visualize the membrane. The membrane is cut abroad along with a tiny pie shaped wedge of musculus. This is chosen membrane resection with myectomy and decreases the chances that the membrane will grow back. Muscular subaortic stenosis is a more diffuse narrowing that sometimes involves the mitral valve. The operation is performed in the aforementioned manner as detached subaortic stenosis using the heart lung bypass machine. The surgeon incises the aorta and looks through the aortic valve to cutting away the thickened muscle tissue. Care is taken to avoid the mitral valve structures. This type of narrowing is more than difficult to care for and another operation to overstate the entire left outflow tract may be required at a afterward time. Surgery for supravalvar aortic stenosis: An incision is made downward the center of the breastbone and the heart is stopped for a brief menses of time while a center lung bypass automobile supports the body. The surgeon makes an incision forth the length of the narrowing in the aortic wall. A patch is then placed into the area where the incision was made to open up the area and relieve the narrowing. The size and length of the patch is adamant past the caste of narrowing of the aorta.
Long term outlook for children with aortic stenosis
Overall, the outlook for people with aortic stenosis is very skilful. Since it is a lifelong problem that tends to progress over time, people with aortic stenosis need to see a cardiologist on a regular basis.
Have the next step
The University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital is a leader in treatment of aortic stenosis. For more information on our programs and services, or to brand an date, delight call i-877-475-6688.
Clinics
Care and services for patients with this problem are provided in the Congenital Heart, Interventional Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery clinics at the University of Michigan Medical Center in Ann Arbor. What is the outlook for children with aortic stenosis? Overall, the outlook for people with aortic stenosis is very practiced. Since it is a lifelong trouble that tends to progress over time, people with aortic stenosis need to see a cardiologist on a regular basis.
References
Galal O. Rao PS, Al-Fadley F & Wilson Advertisement. Follow-upward results of balloon aortic valvuloplasty in children with special reference to causes of late aortic insufficiency. American Middle Periodical 133:418-27, 1997. Lupinetti FM, Pridjian AK, Callow LB, Crowley DC, Beekman RH & Bove EL. Optimum treatment of discrete subaortic stenosis. Ann Thorac Surg 54:467-seventy, 1992. Mendelsohn AM & Shim D. Inroads in transcatheter therapy for congenital heart disease. J Pediatr 133:324-33, 1998. Rocchini AP. Comparison of risks and short- and long-term results of airship dilatation versus surgical treatment for pulmonary and aortic valve stenosis and restenosis and coarctation and recoarctation of the aorta. Curr Stance Pediatr v:611-viii, 1993. Written by: S. LeRoy RN, MSN, Louise Callow RN, MSN Reviewed September, 2012
mortonhatumer1995.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.mottchildren.org/conditions-treatments/ped-heart/conditions/aortic-stenosis
0 Response to "What Is a Newborn Baby's Heart Valves Upside Down Called"
Post a Comment